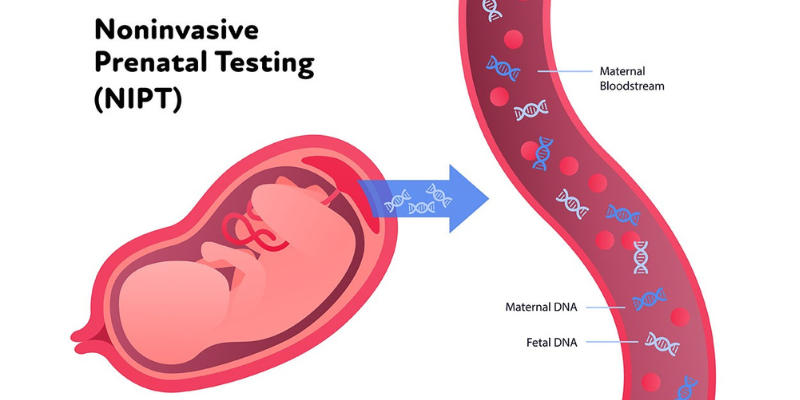
The mother’s blood contains fragments of the baby’s DNA. Noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT) determines a baby’s risk for several genetic abnormalities, including Down syndrome, by performing a straightforward blood test that examines that DNA (cell-free DNA, or cfDNA).
NIPT is a prenatal screening that determines whether there is a higher chance of giving birth to a child with a genetic condition by analysing DNA from the baby’s placenta in a mother’s blood sample. However, a test like NIPT can only identify the likelihood that your child has a chromosomal issue, not if it is present. But for three of the most prevalent illnesses, its accuracy ranges from 97 to 99 percent.
Your doctor and you can decide on the next course of action, including whether to have a diagnostic test like chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis (“amnio”), based on the findings of an NIPT screening. These genetic tests determine if a newborn has a chromosomal problem with 100% confidence by analysing the genetic material of the infant, which is extracted from the placenta or amniotic fluid. A NIPT is safe for both the mother and the child because it just requires a brief blood sample using a needle and syringe. After the sample is transported to a lab, a technician will examine the blood’s cfDNA for any indications of anomalies.
In order to decide whether more testing is required, the doctor will probably compare the results of the NIPT with those of the first-trimester or nuchal translucency screening. If the result is positive, the physician could suggest amniocentesis or CVS as a follow-up procedure to confirm the findings and look for any further issues that NIPTs might miss.
Common mistakes in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) can vary, but here are a few examples:
The neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) plays a crucial role in providing specialized medical care to newborn infants who require intensive medical attention. The clinical importance of the NICU includes:
When speaking with a NICU nurse, here are some questions you may consider asking:
Yes, neonatal intensive care (NIC) is the same as the NICU (Neonatal Intensive Care Unit). The NICU is a specialized unit within a hospital where newborn infants who require intensive medical care are treated. The terms “neonatal intensive care” and “NICU” are often used interchangeably to refer to the specialized medical care provided to critically ill or premature newborns.
In the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), specialized medical care is provided to newborn infants who require intensive monitoring, treatment, and support. Here are some of the activities that typically occur in the NICU: